How blockchain can really change the world of clinical trials?
In clinical trials, monitoring is one of the most important requirements. You have to ensure that a clinical trial is conducted according to the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) for Human Use guidelines and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) regulations. The setting guarantees the safety of the participants and that the final study data are scientifically correct to demonstrate the efficacy of a new investigational therapeutic intervention. Within clinical trials, there is still room for innovation and digitalization using the latest technologies, such as Blockchain. This technology offers benefits in terms of economics, ecology, and particularly on the integrity of a trial. The massive quantity of data generated in clinical trials is often very personal and therefore sensitive. Errors in the data or a breach in security can have major consequences. This is where blockchain is so useful as it can contribute to both the integrity of the data and its protection.

Blockchain
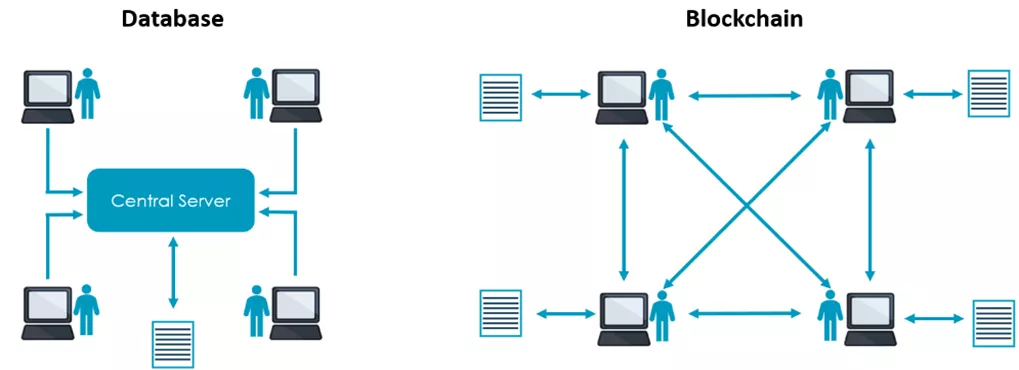
Several researchers have already used blockchain, for example in the management of Electronic Health Records (EHRs), the maintenance of protocols and data management in clinical trials. Blockchain allows to store and share data without being altered and accessible to everyone in the network. This is always traceable through a verifiable timestamp. Data stored on a blockchain is decentralized (Figure 1), so no third party (e.g. someone who maintain the database and provide a service) is involved.
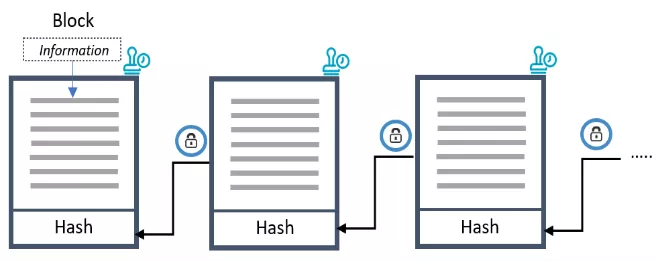
A blockchain is built up of a growing number of blocks, with a new block being linked to the previous one. These blocks contain four different elements: the information, the hash of the current block and of the previous block, a kind of identification number, and the timestamp (Figure 2).
Furthermore, there are also different types of blockchain, from open to private or in between. When using blockchain for storing and sharing data in clinical trials, the choice naturally falls on private, where the participant must request access to the network.
Contribution of blockchain in clinical trials
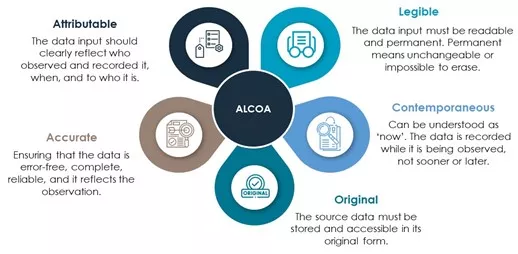
In terms of data, blockchain can certainly contribute to its integrity. Indeed, it satisfies many points of the ALCOA principle. Data integrity (DI) within the pharmaceutical industry is crucial to bring a confidential and efficient product to the market. The ALCOA principle is often used to meet the requirements of DI. ALCOA stands for Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original and Accurate (Figure 3). The timestamp within the blockchain together with the hash contribute to attributable and contemporaneous. Furthermore, the information in the blockchain cannot be modified which makes it original. For legible and accurate, it depends on the system that is built around it and the training of the people who work with it to be compliant.
That being said, blockchain can contribute to many other aspects of the digitalization of clinical trials. First and foremost, blockchain could be a secure technology for sharing data between patients, investigational sites and sponsors. Moreover, clinical trials can be built entirely on the blockchain. The contained information is always accurate and up to date. For example, the latest version of the informed consent will always be available so there will never be incorrect versions signed and therefore no delay in the trial will occur. In addition, the blockchain can be created to automatically generate investigational site files and trial master files, which increases the reliability of these two files and thus the integrity of the trial data. Blockchain can also contribute to the security of the participant. It’s a well-protected technology against intruders and that can store information anonymously. Moreover, because data sharing will be more controlled and will happen much faster, anomalies like adverse events, can be caught more quickly, which reduces the risk for the participants. Further, blockchain can, apart from clinical trials, ensure patients receive more personalized treatments as individual information becomes completely partial on a network. It is possible to set up a nationwide blockchain network, in which a doctor has access to all medical information connected with his patient, a nationwide EHR.
A nationwide network network could also allow a better recruitment process at the start of a trial by better contacting participants who meet the inclusion criteria and accelerate the start of the study, reducing the cost. Only GDPR-wise each participant must give permission for this. In addition, the data placed on the network is easier to trace by the addition of a timestamp to each transaction. All of this will ultimately contribute to the quality and integrity of data obtained during a clinical trial.
Limitations of blockchain
Technological limitations to blockchain mainly relate to the energy-consuming aspect and the slow transaction speed associated with blockchain. However, blockchain is a very recent technology, it is still in full evolution and its general adoption is hindered by a lack of understanding of its principles and its ways of working which creates suspicion. What is good to know is that the scalability and speed of transactions can be increased when creating a good blockchain with a specific purpose. And the blockchain will still be maintained by a developer.
So, should we implement blockchain in clinical trials?
When digitalizing processes within the life science industry, one should always look at the latest technological possibilities available as well as the related guidelines and regulations for a compliant implementation. Digitalization within clinical trials or within the life science sector using personal data can only evolve if knowledge and regulation works closely together to look at the possibilities and limitations of new technologies, such as blockchain. The biggest hurdle in digitalizing clinical trials is the security of the data being shared; these are protected by GDPR legislation. This is where blockchain can contribute greatly.
Written by

- Gilles De W., Consultant, Life Sciences industry
