Smart Logistics taking the express way…
Whether it is driven by the effects of the COVID pandemic, the rise of energy prices or the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions, the Transport & Logistics sector is facing an era of unprecedented challenges. At the same time, innovative technologies are evolving at a never encountered speed. Smart logistics is breaking through and offers endless possibilities to improve efficiency or reduce cost and CO2 emissions.
How can cargo companies accelerate transformation?
The cargo industry is now on the edge of being revolutionized. This article provides some insights on how cargo companies can use data-driven technologies or smart logistics to accelerate their operational & digital transformation, drive growth and increase sustainability. A few examples are worth exploring…

Hurrying the digitalization
On a global scale, millions of shipments are handled every day by shipping, rail, road and air freight companies. The massive flow of goods creates a huge amount of data. In the past decades, cargo firms have been digitalizing this data by stepping away from manual paper-based processes causing inefficiencies and errors. But a series of worldwide events have prompted the digital rush…
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to disrupted global supply chains, new ways of digital collaboration and the explosion of e-commerce. Customers are demanding more speed, accuracy and real-time information. Transportation firms need to explore new ways to enhance digital customer experience.
The European Green Deal, presented in 2019, has the ambition to make the EU climate neutral by 2050 and reduce transport-related CO2 emissions by 90%. To reach this goal, massive efforts are needed from the cargo industry (now responsible for about 8% of global carbon emissions). The growing final consumer’s demand for sustainable products & services is reinforcing the pressure for de-carbonization and technological innovation.
The Ukrainian conflict, along with international trade sanctions, has added new troubles. Cargo firms have to deviate routes, deal with world-trade uncertainty but most of all face a dramatic increase of fuel costs. This is having an overwhelming domino effect: higher prices are passed from carrier to final consumer. Cargo companies are looking at digital solutions to reduce overall rising costs.
What can cargo firms do to succeed in operational & sustainable transformation?
To navigate in this challenging context and gain a competitive advantage, cargo firms should accelerate their operational transformation, and set sail for smart logistics! The concept commonly refers to the use of new technologies to enable a more intelligent, efficient and sustainable way to plan, manage and control logistic activities.
How can this be realized? As we believe that a successful transformation starts with data, the following steps are essential:
#1 (Re)define a clear digital roadmap, targeting 100% digital & real-time data. It helps to exploit innovative technologies in a coordinated way and assure initiatives are in line with the overall business strategy.
#2 Perform a data maturity assessment across business units. Evaluating the capability to deal with the creation, storage, handling and sharing of data is essential to identify key development areas, take action and leverage the overall benefits of digital transformation.
#3 Outline a data governance model that clarifies the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders, and emphasizes the value of data-sharing. Without a framework, it is difficult to manage data flows and break silos in the sharing of data, in and outside the company.
#4 Select the right tools, technology and software, following the service-oriented architecture (SOA) principles. Web-service solutions provide features that can be reused for other tools and support seamless integration with internal applications or external platforms. They create the ability to quickly respond to variations in digital ecosystems.
#5 Use appropriate methodology & industry best practices as they have shown to be more effective than trial and error, or became a standard way of doing. Integrating these concepts in project management leads to better and faster results, lowering of risks and maximization of investments.
#6 Capitalize on the value of data-sharing, with the aim to develop collaborative services and offer Logistics as a Service (LaaS) solutions. By developing Software as a Service (SaaS), Cargo companies can extend their business models from traditional transportation to integrated services offering extra visibility, efficiency and collaboration.
#7 Set ambitious sustainability goals and fast-track actions to mitigate emissions of greenhouse gases. By investing in technology to measure, analyze and reduce CO2 emissions, cargo companies can win the race to carbon neutrality and create a decisive competitive advantage.
How can data-driven technology be used?
To unleash the full potential of smart logistics, one word is key again: data! Let’s have a look at some data-driven technologies and analyze how their interactions (sometimes overlapping) can create a virtuous cycle of growth and efficiency improvement. Concrete examples are illustrating how technology can be translated into actionable projects.
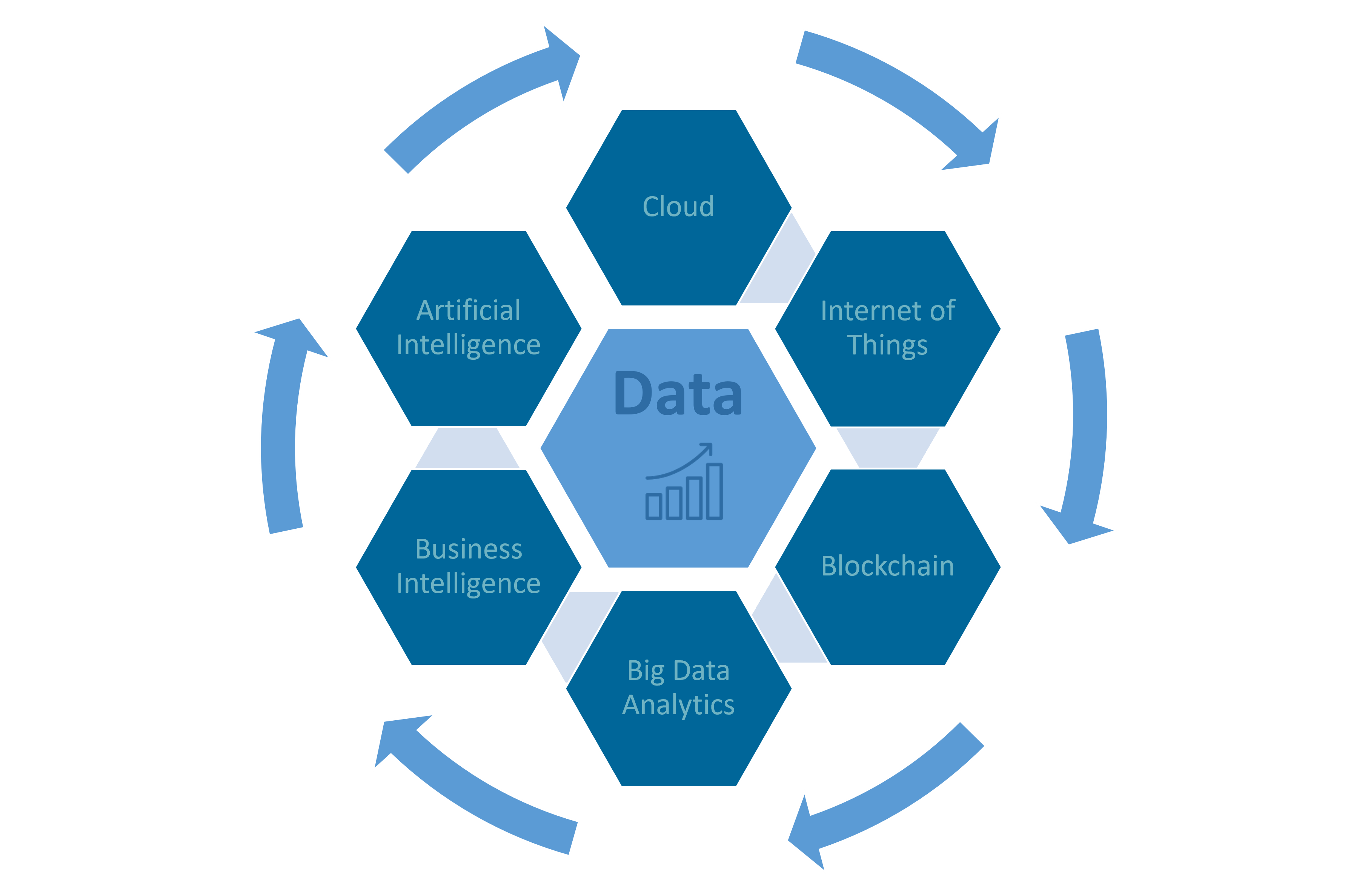
Diagram: Data creating a virtuous cycle of growth & efficiency improvement | Source: Hugues De Cooman (Avertim)
A. ‘Cloud'... and the decrease of data handling costs
Cloud refers to a network of servers, software and related equipment. By using Cloud Services, cargo companies don’t have to manage their own IT infrastructure and can store vast datasets without massive investments. With the rise of cloud-based applications, benefits are not limited to cost-efficient and reliable data storage but extend to data exchange. This is enabled by software protocols called Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), tending to replace traditional Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
Through the use of cloud-based platforms, cargo companies can exchange data with external parties like customers or third-party providers. These platforms can resolutely improve operational efficiency. They allow actors along the transportation network to integrate and scale software services, hence catalyzing the benefits of the cloud.
B. ‘Internet of Things’ … and the explosion of real-time data
Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices that are collecting and exchanging data through advanced sensor technology. IoT enables to connect an ever-increasing number of products and physical devices. In combination with new wireless technology and 5G data networks closing remaining connectivity gaps, the IoT brings real-time visibility to transportation networks.
Cargo companies can use connected containers to generate real-time and geo-localized data. By equipping Unit Load Devices (ULDs) or individual pieces with sensors and GPS trackers, the transport status and conditions can be monitored all along the shipment lifecycle. The real-time visibility facilitates proactive intervention or impact minimization in case of troubles or delays. It can also offer additional information to analyze and share the carbon footprints of transported goods.
C. ‘Blockchain’ … and the intensification of data-sharing
Blockchains refer to cloud-based digital ledgers where transactions, interactions or authentications are recorded and verified by a network, rather than by a central authority. It enables to share data in a more transparent, reliable and traceable way. Being publicly accessible or restricted, they offer opportunities for empowered collaboration with customers, external organizations or customs, security and safety administrations.
Cargo companies can use permissioned blockchains to share customs declaration documents with regulatory authorities. This can streamline the customs clearance processes, reduce the number of litigations and considerably improve operational efficiency.
D. 'Big Data Analytics' ... and the valorization of information
Big Data Analytics refers to the process of collecting and analyzing vast quantities of data. As growing datasets become too large and complex to be handled by traditional data-processing software, cloud-based Big Data Analytics offers scalable and affordable solutions to turn data into information assets. Cargo companies might not realize it, but they are sitting on a mine of exploitable data that can be attractive to many parties and potentially generate additional forms of revenue.
Cargo firms can use Big Data for environmental data analysis and carbon profiling. The monitoring, analysis and publication of CO2 emissions can help to identify areas of improvement and create awareness. It offers opportunities to adjust de-carbonization strategies to rising technologies and adopt more sustainable practices like the expansion of multi-modal transport (combining road, air, rail and truck in an optimized way).
E. 'Business Intelligence' ... and the rise of data-driven decisions
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the process of transforming data into actionable information and decisions. The rise of cloud-based BI technologies offers improved solutions to visualize datasets, identify trends and drive decisions. BI tools can also be used for predictive analysis. Gathering past performance and combining it with real-time data enables projections on future trends or long-term strategies.
Cargo companies can use BI-enriched track-and-trace tools to provide real-time visibility and better insights into issues such as disruption or on-time performance. The embedding of BI Technology creates opportunities to create automatic alerts or self-service reports. It can optimize the decision-making process via advanced forecasting or transport route optimization, possibly leading to additional CO2 reductions.
F. 'Artificial Intelligence' ... unlocking the full potential of Big Data
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to a set of interacting technologies which allow equipment to interpret data, learn automatically from patterns and automate decisions. By combining big datasets with fast repeated processing and advanced algorithms, AI can improve the performance of machines or autonomous vehicles, and ultimately help them to outperform human actions and decisions.
Cargo companies can use AI to set up smart terminals. AI enables to analyze movement and (off)loading data sent by IoT-connected vessels or containers. By integrating this information with operational data, combining it with recorded patterns and automating the decisions, can increase productivity, optimize traffic, resource or storage capacity and even lower CO2 emissions.

To conclude …
The transport sector is facing extraordinary challenges of growing customer expectations and urgent cost & CO2 reductions. At the same time, revolutionary technologies are emerging and already offer concrete actionable solutions.
Cargo companies should not miss the train of smart logistics. To do so, we believe they should (further) accelerate operational digitalization, through a structured approach for handling and sharing data.
Cloud, Internet of Things, Blockchain, Big Data Analytics, Business and Artificial Intelligence, … All these technologies can generate an exponentially growing amount of data. By cascading them into projects, aligned with a clear strategic & digital roadmap, they will trigger a virtuous cycle of growth and efficiency improvements…
We are finally convinced that the full potential of smart logistics can only be exploited through the valorization of information through collaborative services and digital networks, and the focus on sustainable digitalization.
As sustainability might become the biggest disrupting factor in the cargo industry, our strong belief is that more collaborative, transparent and greener strategies will lead to competitive advantages! Our sincere hope is that data-driven technology will very rapidly contribute to a more sustainable, circular future for transportation and logistics...

Written by
Hugues D., Senior Lead Consultant | Transportation & Mobility
