COVID-19 Tracker
Status of the Top 5 vaccines candidates
Avertim has a vast experience in the pharmaceutical and especially the vaccines industry. Therefore, we are closely watching the development of COVID-19 candidates and working with some of the leading companies to plan activities such as manufacture ramp-ups. In this article, find out more about the latest development of the most advanced vaccine projects, often lead by partnerships of leading pharmaceutical development and manufacturing companies.

Over 230 vaccines
The WHO tracks the global research efforts against COVID-19 and continuously reports on their progress. As of March 2021, there are more than 270 vaccines against COVID-19 in different stages of pre-clinical and clinical development (see Figure 1 or read our previous article). Scientists and companies are currently testing 83 vaccines in clinical trials (Phase I, II and III) and although some vaccines have received emergency use authorization, no vaccine was fully approved yet.
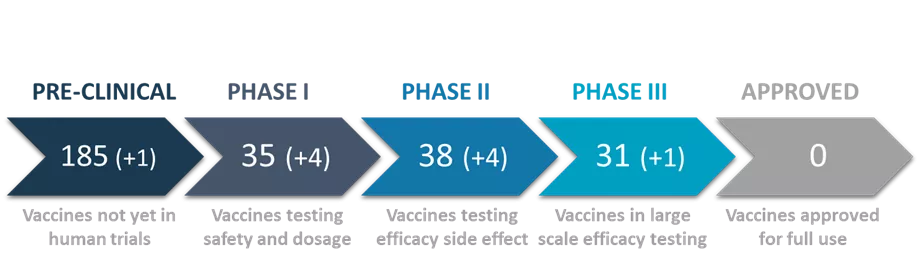
Figure 1: Number of currently developed vaccines worldwide. Based on WHO’s data on April 30th.
What’s new?
The world is still worried by the emerging coronavirus variants, especially the ones from the UK and South Africa who both appear to be more contagious. The South African and UK variant show multiple changes in the spike protein. This protein enables the virus to enter, thus infect, human cells. These changes have not altered the spike protein shape and ongoing studies aim to confirm the effectiveness of the current vaccines. Moreover, a new coronavirus variant, discovered and currently spreading in California appears to be more contagious than previous variants. This strain produces double the amount of viral particles and might be more resistant to the approved vaccines.
In February, the FDA issued official recommendations to vaccine producers to study the impact of COVID-19 variants on the efficacy and performance of their product. Next, the FDA also declared that large scale clinical trials are not necessary for the authorization of vaccines that are modified to tackle coronavirus variants. In addition, vaccine producers struggle to manufacture and deliver enough vaccines around the world. More and more pharma companies are combining their efforts to support the manufacturing.
In April, a second giant coronavirus wave struck India. The currently battling country will receive aid from the United States in the form of extra vaccines, additional raw materials to produce vaccines, therapeutics, rapid diagnostic tests, ventilators etc. A new variant has been discovered in India and preliminary studies show a decreased effectiveness for both Pfizer and Moderna’s vaccine.
In the meantime, Biden’s administration is in favor of COVID-19 vaccine waiver. Both Moderna and Pfizer’s CEO are opposed to a patent suspension.
Due to the crushing covid wave, India won’t conduct local trials for the Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson and Moderna vaccines in order to speed up the roll-out.
To keep track of the emerging corona variants, the WHO has renamed the four high-priority variants using Greek letters. Respectively, the UK, South Africa, Brazil and India variant are named as the Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta variants from now onwards.
In June, the world’s 7 richest countries, the G-7 have agreed to donate 1 billion vaccine doses to poorer nations over the course of 2022 with the US providing half of the vaccines.
To find out more about the information from the past months

#1 BioNTech-Pfizer-Fosun Pharma
With BNT162 RNA Vaccines
The most advanced vaccine projects worldwide in clinical development. The German biotechnology company BioNTech is working in cooperation with Pfizer and Fosun Pharma on developing its RNA vaccines BNT162, which entered a combined phase I/II clinical trial in early May and is currently in a phase II/III trial.
WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
End of May, Pfizer received the green light from the UK for 12-15 year-olds, following the trend from Europe, US and Canada.
Beginning of June, CEO Albert Bourla tweeted that Pfizer started dosing children aged 5 to 11 in their new stage 3 trial and plans to expand it to children as young as 6 months.
From a study done by Public Health England it could be concluded that two doses of the Pfizer or AstraZeneca vaccine are highly effective (respectively 96% and 92%) against the Delta (Indian) variant.
The recent rare reports of myo-or-pericarditis in people who received the Pfizer vaccine has resultant in an emergency meeting of the CDC advisory committee.
PREVIOUSLY
Mid May, Pfizer & BioNTech announced they will donate vaccines for Olympic athletes and officials preparing for Tokyo to be fully vaccinated for the games.
Next, they announced the initiation of a Biologics License Application with the FDA to fully approve their vaccine.
The EU and Pfizer & BioNTech signed a new contract for the delivery of 1.8 billion doses of COVID vaccines for 2021-2023.
After new stability studies, the EMA declared that the Pfizer’s vaccine vials can now be stored at in a normal fridge (2-8°C) up to one month, allowing more flexibility.
On the 19th of April, Pfizer announced that they will supply an additional 100 million doses of its vaccine to the EU member states in 2021.
In the meantime, Pfizer has confirmed the first occurrence of counterfeit versions of its vaccine, seized in Poland and Mexico.
Beginning of May, the chief of BioNTech declared that in partnership with Pfizer, they will be able to produce 0,5 billion more than previously set target of 2,5 billion doses in 2021 thanks to the ramped up manufacturing.
Meanwhile, the EMA initiated an accelerated assessment of the Pfizer vaccine for young adolescents aged 12 to 15 and expects its recommendation in June.
To find out more about the information from the past months
#2 AstraZeneca-Oxford University
With ChAdOx1-S vaccine (another name AZD1222)
The British-Swedish company AstraZeneca and the University of Oxford are developing a vaccine called ChAdOx1-S using viral vector technology.

WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
End of May, the FDA declared it may no longer review new vaccines for emergency use authorization during the pandemic. AstraZeneca among others have started discussions with the regulatory body.
The UK health minister confirmed discussions with AstraZeneca concerning a modified Covid-19 vaccine to target the beta variant (South African variant).
From a study done by Public Health England it could be concluded that two doses of the Pfizer or AstraZeneca vaccine are highly effective (respectively 96% and 92%) against the Delta (Indian) variant.
PREVIOUSLY
Mid-May, AstraZeneca announced it will skip an emergency use approval from the FDA and seek full FDA approval instead.
Meanwhile, the relation between AstraZeneca and the EU remains difficult since the EU launched a new lawsuit against the pharma giant. In addition, AstraZeneca’s contract with the EU will expire in June.
Mid April, Spain announced that it will test the effect of mixing a first shot of the AstraZeneca vaccine with a second shot of the Pfizer vaccine since the country restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in people over 60. The trial will consist out of 600 people of all ages.
End of April, Indian government sources confirm that India will receive the largest share of the 60 million doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine that the US intends to share globally.
AstraZeneca’s vaccine is still suffering to gain confidence in Europe with some countries limiting its use in people under 60 years of age.
AstraZeneca’s vaccine has now an official name: Vaxzevria.
On March 4th, EU and Italy blocked the export of 250 000 doses to Australia.
According to an opinion poll, Europeans are less confident about AstraZeneca's vaccine than the Pfizer and Moderna vaccine.
Mid March, AstraZeneca is preparing the files to request emergency approval for its vaccines in the US.
AstraZeneca could get an emergency approval from the FDA in April. Data from 32 000 patients are being analyzed.
On March 18th, the EMA confirmed that the benefits from AstraZeneca’s vaccine outweigh the risk, despite the possible link to rare blood clots. This information came after several European countries paused the vaccination with AstraZeneca’s vaccine.
To find out more about the information from the past months

#3 Moderna-NIAD
With mRNA1273 vaccine
The U.S. biotechnology company Moderna is developing RNA vaccines in cooperation with NIAD and moved the first COVID-19 vaccine into a human clinical trial in March.
WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
End of May, Moderna announced that in their phase 3 trials in teenagers (12-17 years old) reached 100% efficacy. These stellar results could lead to back-to-school FDA approval in the coming months. In June, Moderna started seeking approval for their vaccine in adolescents in the European Union as well as Canada and is planning to seek approval in the US in early June
After the rollout of the vaccine under emergency use authorization, Moderna said on June 1st to seek full FDA approval of their vaccine.
On June 10th, Moderna is seeking emergency use authorization for their vaccine in teenagers between age 12 and 17 based on the results of their late-stage trial. Similarly, they are seeking authorization in the EU.
PREVIOUSLY
Moderna has generated $1.73 billion in revenue from its COVID vaccine.
Mid April, new trial data shows the vaccine is 90% effective in preventing symptomatic COVID as well as 95% effective against severe cases of the virus. Currently, Moderna is testing specific boosters and collecting data on the vaccine’s use in adolescents.
The WHO declared that it will review the Moderna vaccine for emergency use authorization on Friday 30th of April.
End of April, Moderna asked Swiss Nestlé employees to volunteer the CDMO Lonza to scale the Moderna production after supply chain delays.
Beginning of May, the WHO gave green light to Moderna’s vaccine for emergency use for adults (>18 years old). By doing this, it can allow other countries to speed up their own approval process.
Meanwhile, to meet its accelerated vaccine supply forecasts, Moderna will at least double its manufacturing capacity in Massachusetts. Currently, Moderna estimated it will produce 800 million to 1 billion doses in 2021.
Mid of April, the FDA has authorized Moderna’s vaccine to be stored at room temperature for 24 hours, once it is removed from the refrigerator. In addition, the FDA authorized a new vial containing 15 doses of Moderna’s Covid-19 vaccine.
The European Union will buy 150 million additional doses of Moderna’s vaccine.
Baxter will provide fill/finish sterile manufacturing services and supply packaging for 60-90 million doses of Moderna’s vaccine.
Similarly to Pfizer’s vaccine, a new study shows that Moderna’s vaccine iseffective in pregnant and lactating women as well as their newborns.
On March 15th, Moderna announced the start of the phase I clinical trial for their next generation vaccine that would be stable at standard refrigerator temperatures.
To find out more about the information from the past months
#4 Johnson & Johnson
With its Ad26.COV2.S vaccine
Johnson & Johnson is developing vaccines using viral vector technology and clinical testing is currently in a combined phase I/II trial launched in July.

WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
End of May, the EMA announced that it is investigating the death of a Belgian woman due to a blood clot after receiving the Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine. Consequently, Belgium has put an upper limit of age 41 on the J&J vaccine.
Meanwhile, the U.K. and Mexico gave green light to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
In the U.S., the rollout of the J&J vaccine was temporarily paused in April, resulting in an enormous stockpile of vaccines that will expire by the end of June. In turn, the FDA extended the shelf life for the vaccine with 1,5 months.
The EMA declared mid-June that they were aware of the cross contaminated batch of active substance for the J&J vaccine at a manufacturing site in Maryland. Out of precaution, the EMA advised to not release vaccines with the active substance made around the same time. However, it is still believed that the batches of released vaccines in the EU were not affected.
PREVIOUSLY
On the 20th of April, due to cases of blood clots and low platelet levels, Johnson & Johnson asked not to use the vaccine until the EMA decision. Luckily, after a favorable risk-benefit analysis from the EMA and a warning on the label, Johnson & Johnson declared it will resume the roll-out of its single-dose vaccine in Europe.
Similarly to Europe, also in the US, the CDC’s advisory committee for immunization practices voted to continue the use of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in adults (<18 years). Also in the US, the vaccine will have a new warning on the label. The CDC and FDA are likely to accept this recommendation.
Due to a human error, up to 15 million J&J vaccine doses were lost in a production plant based in the US. Ingredients from both J&J and AstraZeneca's vaccines were mixed up. Since the AstraZeneca vaccine has not yet received a green light from the FDA, it is important that there are no mix-ups between the vaccines. From now on, only the J&J’s vaccine will be produced in the Baltimore based company, Emergent BioSolutions Inc.
J&J will include adolescents aged 12 to 17 year old in their clinical trial.
On April 13th, the FDA has recommended to pause the use of J&J’s vaccine due to blood clot concerns in adult women.
On Friday, the 1st of March, the FDA granted Johnson & Johnson emergency use authorization for their vaccine in adults. Meanwhile, Johnson & Johnson announced that it will start clinical trials in which the vaccine will be tested on children and infants. Beginning of March, Merck announced that it will provide access to two US production plants to J&J. This deal was facilitated by Biden’s administration, by promising $ 269M in U.S funding, which could double J&J’s vaccine capacity. On March 11th, the EMA approved J&J’s vaccine for emergency use.
On March 15th, Takeda announced they will utilize IDT Biologika GmbH, a CDMO, to manufacture J&J’s COVID-19 vaccine. Takeda is now supporting the production of three different COVID-19 vaccines (Novavax, Moderna and J&J).
To find out more about the information from the past months

#5 GSK-Sanofi
With their SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates
Sanofi is working on recombinant protein vaccines in combination with adjuvants developed by GSK to stimulate the immune system.
WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
End of May, Sanofi and GSK have passed a small phase 2 trial with impressive data on antibody response after which they launched their large phase 3 trial. This vaccine could be a big hit since it combats the emerging corona variants and could lead to full approval by the end of 2021.
PREVIOUSLY
Mid-May, GSK and Sanofi have passed a new phase II clinical trial for their COVID vaccine and are planning a larger phase III for the coming weeks.
Sanofi will help J&J to manufacture their COVID-19 vaccines by giving access to one of Sanofi's plants in France. The plant will produce 12 million doses of the J&J vaccine per month.
End of February, Sanofi and GSK announced that they have not given up and that they are starting a phase 2 study of their vaccine.
CureVac, who recently announced a partnership with GSK and Bayer, initiated rolling submission with the EMA for their COVID-19 vaccine.
To find out more about the information from the past months
Other vaccines to follow
#6 Sinovac Life Sciences
With its inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
The Chinese private company produced an inactivated vaccine, called CoronaVac. The production is based on traditional vaccine manufacturing techniques: virus inactivation. The vaccine supply is eased as it can be stored in regular fridges. CoronaVac is now in phase 3 clinical trials in Brazil, Indonesia and Turkey. It has been approved for emergency use in China since July 2020.

WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
Beginning of June, the WHO authorized the Sinovac vaccine for people older than 18. No upper limit was defined but it should be noted that the effectiveness of the shot could not be determined in people older than 60 due to the small number of participants.
PREVIOUSLY
On April 16th, it was announced that Sinovac's COVID-19 vaccine CoronaVac was 67% effective in preventing symptomatic infection, 85% effective in preventing hospitalizations and 80% effective in preventing death.
On April 1st, Sinovac announced the completion of a third production line increasing the annual capacity to 2 billion doses.
On February 8th, Sinovac received a conditional marketing authorization in China for its COVID-19 vaccine.
Thailand expects to approve the Sinovac’s vaccine for emergency use by the end of February, in parallel to the arrival of the first 200,000 doses.
To find out more about the information from the past months

#7 Sinopharm
With its 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
Sinopharm is a state-owned Chinese company and developed two inactivated vaccines, following a similar inactivation process as Sinovac. Both Sinopharm’s vaccines are in phase 3 trials.
WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
Beginning of June, clinical trial results showed that the Chinese Sinopharm vaccine was successful in preventing symptomatic Covid infections in more than 70% when tested against a placebo. However, it should be noted that most of the trial participants were male and younger than 60.
PREVIOUSLY
Mid-May, the WHO added Sinopharm’s COVID-19 to the vaccine list that are approved for emergency use.
Mid-April, the Sinopharm vaccine was found to be 93% effective in preventing hospitalization and 95% effective in preventing admission to intensive care.
The United Arab Emirates will start to produce the Chinese vaccine from Sinopharm.
On December 30th, phase 3 trials showed an effectiveness of 79%.
In China, already one million people have been inoculated.
To find out more about the information from the past months
#8 Gamaleya Research Institute
With its Sputnik V Adenoviruses based vaccine
The Gamaleya Research Institute is part of the Russia’s Ministry of Health. It developed a COVID vaccine, namely Sputnik V or Gam-Covid-Vac, with an effectiveness of 91.6%. The vaccine is based on adenoviruses containing the gene coding for the spike protein, a similar technology as AstraZeneca and Johnson and Johnson.

WHAT HAPPENED LATELY?
>>Latest update (update 17/06):
Beginning of June, sources revealed to Reuters that the Serum Institute of India is considering to manufacture the Russian Sputnik V vaccine.
PREVIOUSLY
Mid-April, the Gamaleya National Research Center of Epidemiology and Microbiology and the Russian Direct Investment Fund (RDIF) reported that the Sputnik V Covid-19 vaccine showed a 97.6% efficacy, making it the most efficient vaccine.
The WHO announced that it will start inspecting manufacturing practices for the Sputnik V vaccine, together with the EMA starting on the 10th of May.
Mid April, the EMA will investigate the ethical standards of the Sputnik V vaccine trials after allegations were made that some participants may have been forced to participate.
Germany has initiated the discussion with Russia to purchase its Sputnik V vaccine when it is approved by the EMA.
The Sputnik V Covid-19 vaccine has been approved for emergency use in India.
Beginning of March, EMA has started the review of the Sputnik V vaccine. Stelis Biopharma, an Indian company, will produce a minimum of 200 million doses of the Sputnik V vaccine in 2021. There are now 4 Indian companies that are producing the Russian shot, securing 750 millions doses of the Sputnik V vaccine.
